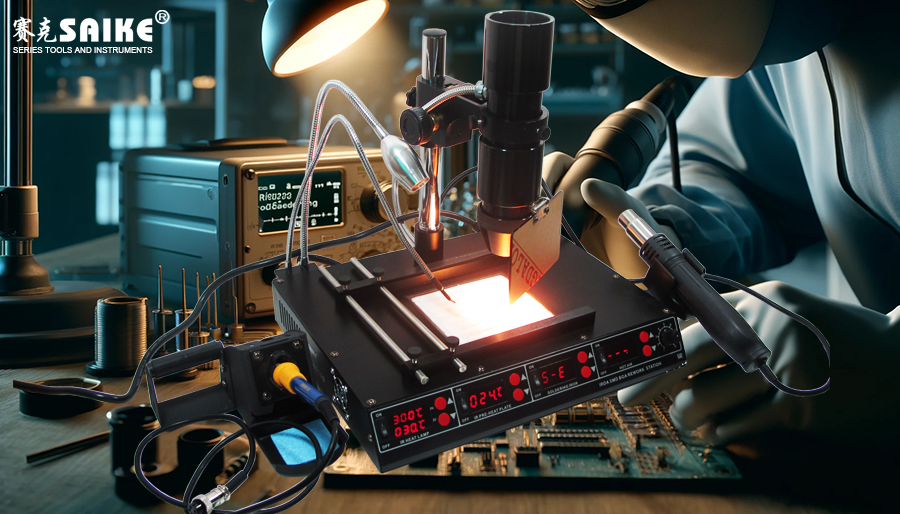
SK-YJ000HWXCHT-KP 100002
In electronic manufacturing and maintenance, desoldering is an important process for replacing and repairing electronic components. Two common desoldering methods are infrared and hot air techniques. There are significant differences between the two in terms of working principle, application scenarios, and operational performance. This article compares infrared and traditional hot air desoldering methods and analyzes the advantages of infrared technology in detail.
I. Comparison of Working Principles
1.Infrared Desoldering:
– Uses infrared radiation to heat solder joints or components. Infrared transfers heat through direct radiation, heating the target object, and the solder joints absorb infrared energy and convert it into heat.
2.Traditional Hot Air Desoldering:
– Uses a hot air gun to blow hot air to heat the circuit board and solder joints. The hot air is directly transmitted to the solder joints, melting the solder and separating the components from the circuit board.
II. Comparison of Application Scenarios
1.Infrared Desoldering:
– Suitable for desoldering operations of high-density packaged components (such as BGA, QFN, CSP, etc.) and multilayer circuit boards.
– Especially suitable for sensitive electronic components, which are less likely to cause thermal damage to components and circuit boards.
2.Traditional Hot Air Desoldering:
– Suitable for desoldering larger, simpler packaged components, such as DIP and SMD packages.
– Due to the easy diffusion of hot air during heating, it may not be suitable for high-density packaged components or operations adjacent to other sensitive components.
III. Performance Comparison
1.Temperature Control:
– Infrared Desoldering: Has higher temperature control accuracy, can accurately adjust the radiated heat, and monitor the temperature of the solder joints in real-time through temperature sensors to ensure that the temperature curve meets the requirements.
– Hot Air Desoldering: The temperature control is relatively less accurate than infrared. The heating area is larger, making it difficult to achieve precise heating of specific solder joints.
2.Heating Uniformity:
– Infrared Desoldering: The radiated energy can be evenly distributed in the solder joint area, reducing hot and cold spot problems.
– Hot Air Desoldering: The flow of hot air can cause temperature unevenness in the heating area, especially at high wind speeds.
3.Heating Speed:
– Infrared Desoldering: Can transfer heat quickly and uniformly, with high heating efficiency.
– Hot Air Desoldering: The heating speed is slower, especially at low wind speeds.
4.Impact on Components:
– Infrared Desoldering: The energy is concentrated at the solder joints, making it less likely to damage adjacent components.
– Hot Air Desoldering: The diffusion of hot air can easily cause thermal damage to adjacent components or circuit board areas.
IV. Advantages Analysis
1.Advantages of Infrared Desoldering:
– Precision: Precise temperature control, suitable for high-density and complex packaged components.
– Uniformity: The heating is uniform, which is less likely to cause local overheating or cold spots.
– Safety: Less damage to sensitive electronic components, improving the success rate of rework and maintenance.
2.Advantages of Hot Air Desoldering:
– Versatility: Suitable for desoldering and soldering various packaged components.
– Economy: The equipment cost is relatively low, suitable for small-scale maintenance or laboratory applications.
V. Conclusion
Infrared and traditional hot air desoldering methods have their respective advantages in different application scenarios and technical requirements. When precise operations are required for high-density packaging or multilayer circuit boards, infrared desoldering has obvious advantages in terms of precision, uniformity, and safety. For larger and simpler component desoldering, hot air desoldering is still an economically effective choice. Understanding their respective characteristics and advantages can better choose suitable desoldering tools for different maintenance tasks.


