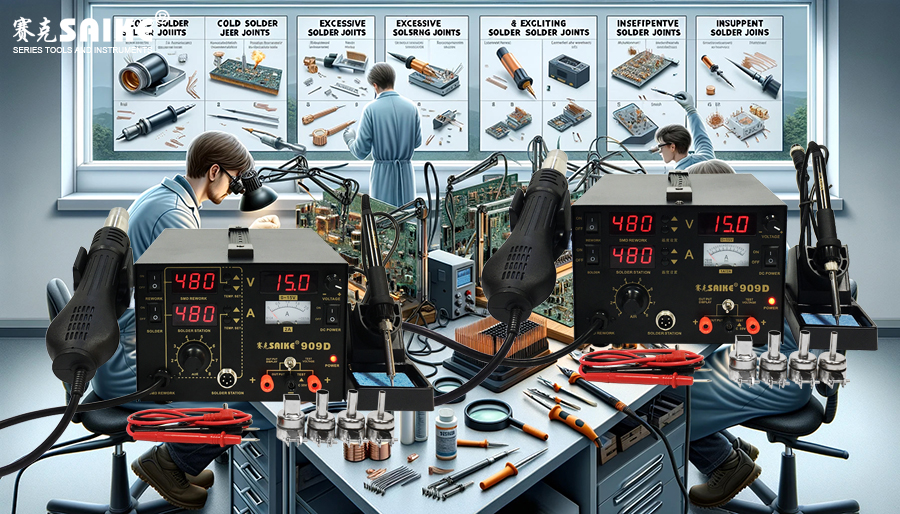
SK-YJ000RFSHY-KP 100025
Soldering is crucial in electronic engineering, and soldering stations serve as the primary tool. However, various faults may arise during their use. This article will delve into the troubleshooting methods for cold solder joints, excessive solder joints, and insufficient solder joints, aiming to assist technicians in enhancing soldering quality.
I. Troubleshooting cold solder joints
1.Examine common causes of cold solder joints:
– Insufficient solder: The solder pad is not adequately covered, resulting in poor contact.
– Inadequate temperature: The soldering temperature is too low, preventing the solder from fully melting.
– Oxidation issues: Oxidation on the soldering surface hinders the solder’s adhesion.
– Improper operation: The soldering time is too short, or the soldering angle is incorrect.
2.Repair steps for cold solder joints:
– Identify cold solder joints: Use a magnifying glass or microscope to inspect solder joints for cold solder joints.
– Heat and resolder: Adjust the soldering station temperature to an appropriate level (typically around 350°C), reheat the cold solder joint with a soldering iron, and add the right amount of solder.
– Note: Ensure the solder joint is adequately heated to allow the solder to flow and cover the solder joint surface.
– Clean the solder joint: Use a solder sucker or braided copper wire to remove old solder and resolder.
– Apply flux: Spread a suitable amount of flux on the solder joint to enhance the solder’s fluidity and adhesion.
3.Measures to prevent cold solder joints:
– Maintain stable soldering temperature: Ensure the soldering station temperature remains stable within an appropriate range.
– Use high-quality solder: Choose high-quality solder and avoid using poor-quality or heavily oxidized solder.
– Correct operation: Master proper soldering techniques to ensure the solder fully melts and covers the solder joint.
II. Troubleshooting excessive solder joints
1.Common causes of excessive solder joints:
– Excessive solder usage: Applying too much solder during the operation.
– Prolonged soldering time: Soldering for too long, resulting in solder accumulation.
2.Repair steps for excessive solder joints:
– Use a solder sucker: Increase the soldering station temperature (to about 380°C) and use a solder sucker to remove excess solder.
– Method: Align the solder sucker with the solder joint, press the button to suck away excess solder.
– Clean the solder joint: Use braided copper wire to remove residual solder.
– Resolder: Resolder on the cleaned solder joint, ensuring a moderate amount of solder is used.
3.Measures to prevent excessive solder joints:
– Control solder usage: Pay attention to the amount of solder used during soldering; avoid using too much.
– Reduce soldering time: Try to minimize soldering time during operation to prevent solder accumulation.
III. Troubleshooting insufficient solder joints
1.Common causes of insufficient solder joints:
– Insufficient solder usage: Not using enough solder during soldering.
– Low soldering temperature: The temperature is too low, preventing the solder from flowing adequately and covering the joint completely.
2.Repair steps for insufficient solder joints:
– Heat and add solder: Adjust the soldering station temperature to an appropriate level (typically around 350°C), heat the solder joint, and add a suitable amount of solder.
– Note: Ensure the solder fully covers the solder joint, forming a reliable connection.
– Apply flux: Spread a moderate amount of flux on the solder joint to enhance the solder’s fluidity and adhesion.
3.Measures to prevent insufficient solder joints:
– Use solder reasonably: Control the amount of solder based on the solder joint size.
– Maintain a stable soldering temperature: Ensure the soldering station temperature remains stable within an appropriate range, avoiding too low temperatures.
IV. Summary
During the welding process, common problems include false welding, too many or too few solder joints, which not only affect the welding quality but may also cause circuit malfunctions. By understanding and mastering the aforementioned treatment methods, technicians can effectively repair welding failures and improve the stability and reliability of welding. In practical operation, maintaining a stable soldering temperature, using high-quality solder, reasonably controlling the amount of solder used, and operating correctly are the keys to preventing welding problems. Through continuous practice and accumulation of experience, welding technology will continue to improve, ensuring the normal operation and long life of electronic equipment.


