SK-YJ000DDXXQ-KP 100024
The electric solder sucker is a commonly used tool in electronic repair and manufacturing, which can effectively remove excess solder from electronic components. Correct usage of the electric solder sucker not only improves work efficiency but also ensures soldering quality. This article will introduce some efficient solder sucking techniques and point out common operation errors and their correction methods.
I. Efficient Solder Sucking Techniques
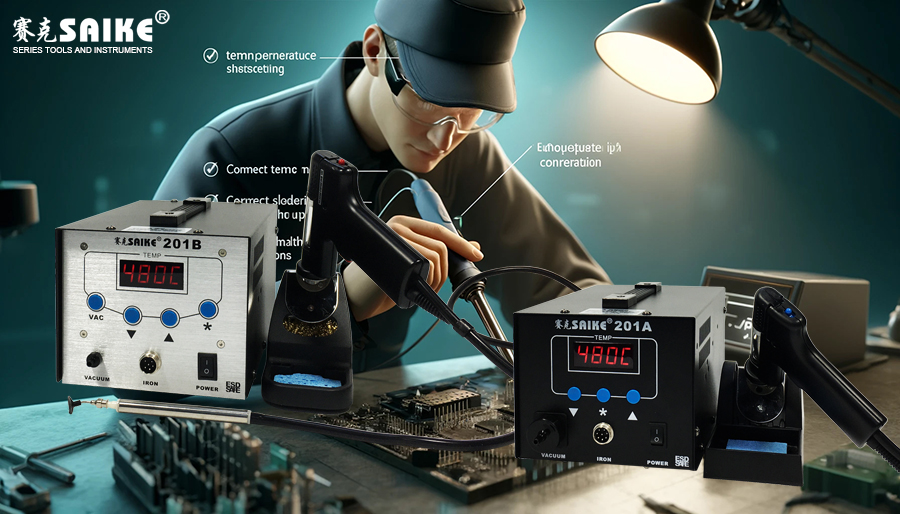
1.Correct Temperature Setting
– Adjust the temperature according to the type of solder and the sensitivity of the board. Too high a temperature can damage the circuit board or components, while too low a temperature cannot effectively melt the solder.
– Quick heating to the melting point of the solder reduces thermal stress on the components.
2.Use Appropriate Soldering Tip
– Choose a tip based on the size of the solder joint. Use a fine tip for small solder joints and a thicker tip for larger ones.
– Ensure the soldering tip is clean before use, with no solder residue or oxide, to maintain good thermal conductivity.
3.Precise Positioning
– Align the soldering tip accurately with the solder joint to be sucked. Ensure the tip completely covers the solder joint to maximize thermal efficiency.
– Stabilize your hand to avoid movement during heating or solder sucking, preventing incomplete solder sucking or damage to the solder joint.
4.Effective Solder Sucking Operation
– Activate the solder sucker instantly when the solder melts for maximum efficiency.
– Try to complete the solder sucking in one operation. Repeated sucking may cause the soldering tip to overheat and damage the solder pad.
II. Common Mistakes and Corrections
1.Improper Temperature Setting
– Problem: Too high or too low a temperature can affect the solder sucking effect, potentially damaging the solder joint or failing to completely melt the solder.
– Correction: Adjust the temperature setting based on the melting point of the solder and the material of the circuit board. Use a thermometer to monitor the temperature of the soldering tip for stability.
2.Incorrect Soldering Tip Selection
– Problem: Using an unsuitable soldering tip can lead to uneven heat distribution, affecting the solder sucking effect.
– Correction: Choose an appropriate soldering tip based on the size and shape of the solder joint. Regularly replace the soldering tip to meet different soldering needs.
3.Slow Solder Sucking Operation
– Problem: Slow operation can cause excessive heat transfer to components and the circuit board, potentially causing damage.
– Correction: Increase the operation speed, ensuring the solder sucker is activated immediately after the solder melts to quickly complete the solder sucking.
4.Insufficient Cleaning of the Soldering Tip
– Problem: Solder residue and oxides on the soldering tip can affect thermal conductivity, reducing solder sucking efficiency.
– Correction: Use a wet sponge or specialized cleaning ball to clean the soldering tip before and after each use. Regularly check the condition of the soldering tip and replace it if necessary.
III. Conclusion
Mastering correct solder sucking techniques and avoiding common mistakes are crucial to improving the efficiency and soldering quality of the electric solder sucker. By practicing these techniques and correcting errors, operators can effectively enhance their soldering skills, ensuring efficient and safe electronic equipment repair and manufacturing processes.