SK-YJ000XYY-KP 100008
I. Best Practices for Configuration
1.Choosing the Right Model and Size
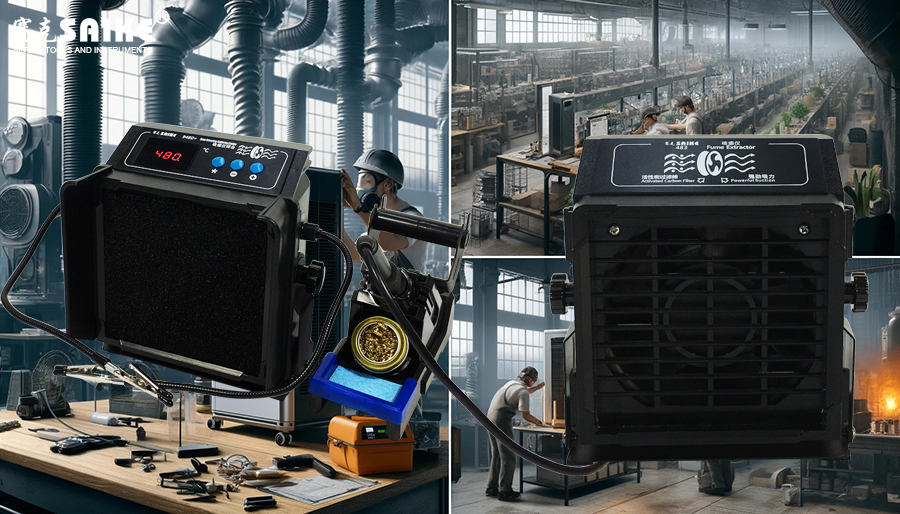
– Select a smoking absorber based on the size of the work area and the amount of smoke produced. For large workstations or high smoke output situations, choose a high-power and large-capacity stationary smoking absorber; for small or highly mobile work environments, portable or desktop smoking absorbers are more suitable.
2.Appropriate Filtration System
– Ensure that the smoking absorber is equipped with a filtration system suitable for specific types of pollution. For example, welding operations require a HEPA and activated carbon composite filter that can filter metal particles and toxic gases.
3.Adequate Airflow and Suction
– Choose equipment that can provide sufficient airflow and suction to ensure that smoke can be effectively captured and processed from the source. The airflow is usually expressed in CFM (cubic feet per minute), so choose the appropriate specifications to maintain efficient suction.
II. Best Practices for Setup
1.Correct Installation Position
– Install the smoking absorber as close to the source of smoke generation as possible, but do not obstruct the operating space in the work area. The ideal installation distance is usually no more than two feet, which can maximize smoke capture.
2.Appropriate Fan Speed
– Adjust the fan speed according to the amount and type of smoke. Most modern smoking absorbers provide variable speed controls to adapt to different working conditions.
3.Regular Maintenance and Inspection
– Regularly inspect and replace filters according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. Clogged filters can reduce the efficiency of the smoking absorber and may cause the equipment to overheat or be damaged.
– Regularly inspect power cords and connections to ensure that all connections are safe and intact.
4.Environmental Factors Consideration
– Consider airflow and other factors in the work environment that may affect smoke behavior. Avoid strong crosswinds or fans from other equipment being directly aimed at the smoking absorber, as this may affect its efficiency.
5.User Training
– Provide appropriate training to employees operating the smoking absorber, including how to operate the equipment, how to perform basic troubleshooting, and when to replace filters.
III. Performance Optimization
1.Monitoring System
– If possible, use smoking absorbers with monitoring functions. These devices can monitor filtration efficiency and machine status in real-time, automatically adjust fan speed, and alert when maintenance is required.
2.Energy Consumption Management
– Use equipment with energy-saving modes, especially during low load periods, to reduce energy consumption and extend equipment life.
3.Feedback System
– Choose a smoking absorber that can provide usage feedback and historical data recording to help optimize operating parameters and predict maintenance needs.
IV. Conclusion
The correct configuration and setup of the smoking absorber are crucial to ensuring its most efficient operation. By following the above best practices, the performance of the smoking absorber can be greatly improved, its service life can be extended, and clean and safe air can be provided for the work environment. Regular maintenance and appropriate operational knowledge are equally important to ensure that the equipment continues to operate in optimal condition.