SK-YJ000XYY-KP 100025
To ensure the effective use and maintenance of smoking apparatus in welding operations, training courses typically cover essential knowledge, operational skills, maintenance procedures, and safety regulations of the smoking apparatus. The following is a review of the key points in the smoking apparatus training course, aiming to help operators fully understand the functions, usage, and maintenance essentials of the smoking apparatus.
I. Basic Knowledge of Smoking Apparatus
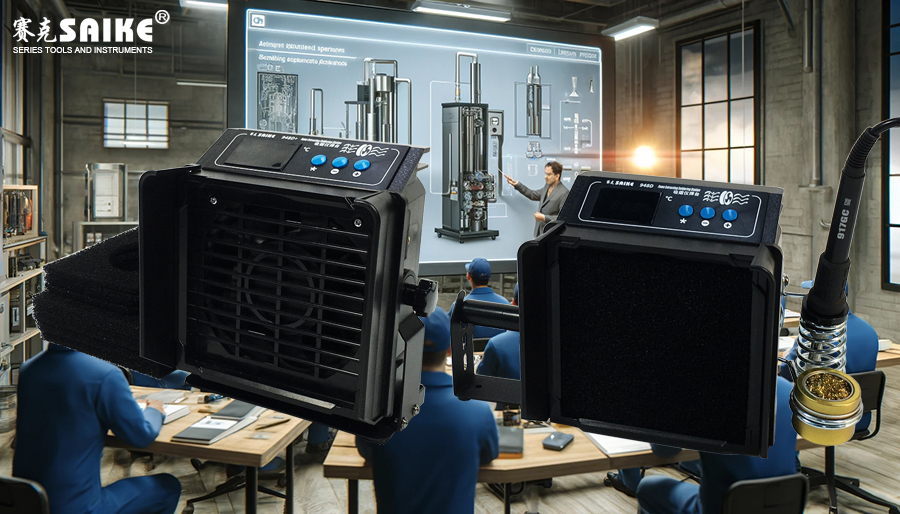
Equipment Overview
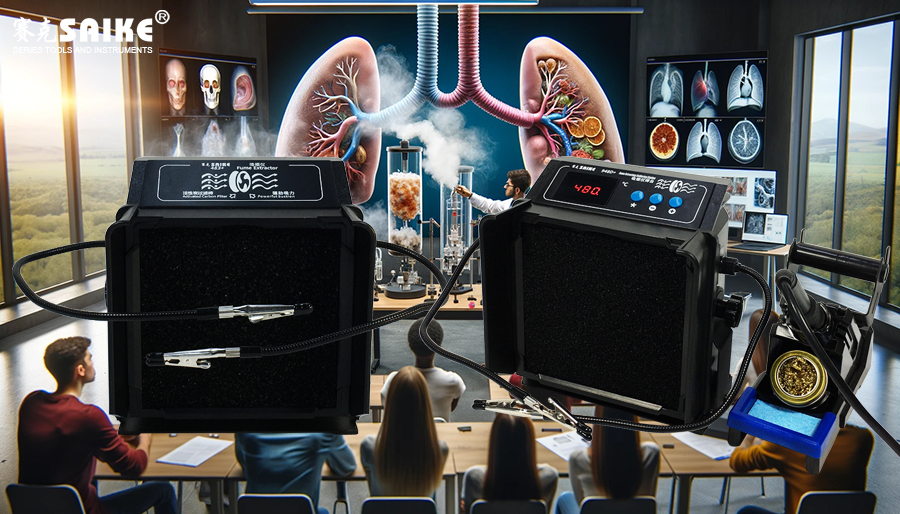
– Functions and Uses: Explain how the smoking apparatus captures and removes harmful substances from welding fumes through a filtering system, protecting the health of operators and
improving the working environment.
– Main Components: Introduce the primary components of the smoking apparatus, including fans, filters (HEPA and activated carbon filter layers), suction nozzles, control systems, etc.
Working Principle
– Suction and Filtering Process: Detailed explanation of the process of air flowing through different filter layers from the suction inlet and the specific role of each layer.
II. Operational Skills Training
Startup and Adjustment
– Startup Steps: Teach how to properly start and shut down the smoking apparatus, including pre-inspection of the equipment.
– Adjusting Wind Speed and Direction: Demonstrate how to adjust the wind speed and suction nozzle direction based on the specific needs of welding operations to achieve the best smoke absorption effect.
Operational Precautions
– Avoiding Common Operational Errors: Emphasize undesirable operational habits, such as covering the suction inlet or placing the suction nozzle incorrectly, which may affect the efficiency of the smoking apparatus.
III. Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Routine Maintenance
– Cleaning and Replacing Filters: Provide detailed guidance on regular inspection, cleaning, and replacement of filters to maintain efficient equipment operation.
– Checking Motors and Fans: Explain the importance of inspecting these components and basic maintenance methods.
Fault Diagnosis and Handling
– Troubleshooting Steps: Provide a series of guides for diagnosing and repairing common faults, such as equipment not starting, suction power weakening, abnormal noise, etc.
– Safe Operation: Emphasize the safety measures that must be followed during troubleshooting, including power-off operations and using the correct tools.
IV. Safety and Compliance
Safety Regulations
– Personal Protective Equipment: Reiterate the need to wear personal protective equipment, such as safety glasses and gloves, when operating the smoking apparatus.
– Compliance with Regulations: Explain the regulations and standards related to the use of smoking apparatus to ensure that operations meet workplace health and safety requirements.
Emergency Response
– Emergency Handling: Teach how to respond correctly in case of smoking apparatus failure or other emergency situations, including emergency shutdown procedures and reporting processes.
V. Summary
Through learning and practicing these training contents, operators will be able to use the smoking apparatus more proficiently and safely, effectively reducing harmful substances in the work environment and improving the safety and production efficiency of welding operations. Regular refresher training and skill verification are also key to ensuring long-term effectiveness and compliance.